Create a multi-zone universe with Kubernetes
YugabyteDB Anywhere allows you to create a universe in one geographic region across multiple availability zones using Kubernetes as a cloud provider.
Prerequisites
Before you start creating a universe, ensure that you performed steps described in Configure the Kubernetes cloud provider. The following illustration shows the Managed Kubernetes Service configs list that you should be able to see if you use YugabyteDB Anywhere to navigate to Configs > Cloud Provider Configuration > Infrastructure > Managed Kubernetes Service:

Note that the cloud provider example used in this document has a cluster-level admin access.
Create a universe
If no universes have been created yet, the Dashboard does not display any.
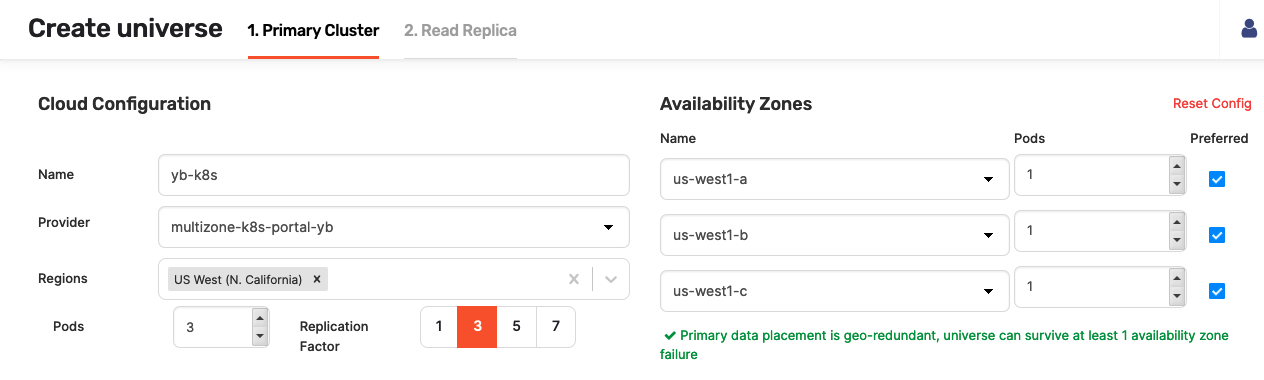
To start, click Create Universe and complete the first two fields of the Cloud Configuration section:
-
In the Name field, enter the name for the YugabyteDB universe using lowercase characters (for example, yb-k8s).
-
Use the Provider field to select the appropriate Kubernetes cloud (for example, multilane-k8s-portal-yb). Notice that additional fields appear.
Complete the rest of the Cloud Configuration section as follows:
-
Use the Regions field to select the region. This enables the Availability Zones option that allows you to see zones belonging to that region.
-
Provide the value in the Pods field. This value should be equal to or greater than the replication factor. The default value is 3. When this value is supplied, the pods (also known as nodes) are automatically placed across all the availability zones to guarantee the maximum availability.
-
In the Replication Factor field, define the replication factor, as per the following illustration:
Configure instance
Complete the Instance Configuration section as follows:
- Use the Instance Type field to select the CPU and memory combination, as per needs to allocate the YB-TServer nodes. The default is small. You can override this setting when you configure the Kubernetes cloud provider (see Configuring the region and zones).
- In the Volume Info field, specify the number of volumes multiplied by size. The default is 1 x 100GB.
- Use the Root Certificate field to select an existing security certificate or create a new one.
- Use the Enable YSQL field to specify whether or not to enable the YSQL API endpoint for running PostgreSQL-compatible workloads. This setting is enabled by default.
- Use the Enable YSQL Auth field to specify whether or not to enable the YSQL password authentication.
- Use the Enable YCQL field to specify whether or not to enable the YCQL API endpoint for running Cassandra-compatible workloads. This setting is enabled by default.
- Use the Enable YCQL Auth field to specify whether or not to enable the YCQL password authentication.
- Use the Enable YEDIS field to specify whether or not to enable the YEDIS API endpoint for running Redis-compatible workloads. This setting is disabled by default.
- Use the Enable Node-to-Node TLS field to specify whether or not to enable encryption-in-transit for communication between the database servers. This setting is enabled by default.
- Use the Enable Client-to-Node TLS field to specify whether or not to enable encryption-in-transit for communication between clients and the database servers. This setting is enabled by default.
- Use the Enable Encryption at Rest field to specify whether or not to enable encryption for data stored on the tablet servers. This setting is disabled by default.
Perform advanced configurations
Complete the Advanced section as follows:
- In the DB Version field, specify the YugabyteDB version. The default is either the same as the YugabyteDB Anywhere version or the latest YugabyteDB version available for YugabyteDB Anywhere.
- Use the Enable IPV6 field to specify whether or not you want to use IPV6 networking for connections between database servers. This setting is disabled by default.
- Use the Enable Public Network Access field to specify whether or not to assign a load balancer or nodeport for connecting to the database endpoints over the internet. This setting is disabled by default.
Configure G-Flags
Optionally, complete the G-Flags section as follows:
-
Click Add Flags > Add to Master to specify YB-Master servers parameters, one parameter per field.
-
Click Add Flags > Add to T-Server to specify YB-TServer servers parameters, one parameter per field.
For details, see the following:
Configure Helm overrides
Optionally, use the Helm Overrides section, as follows:
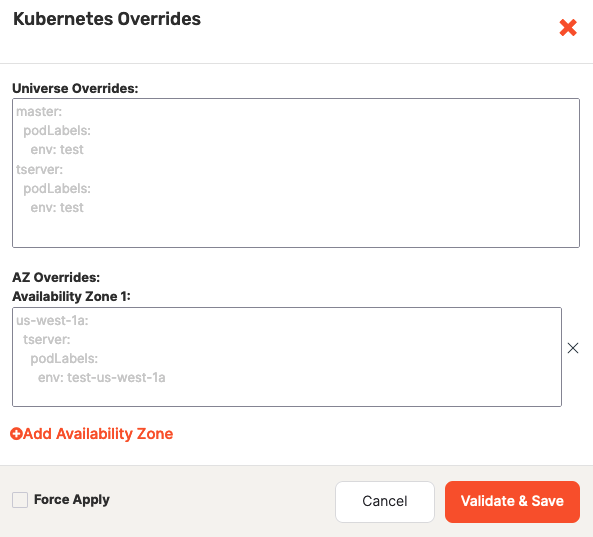
-
Click Add Kubernetes Overrides to open the Kubernetes Overrides dialog shown in the following illustration:
-
Using the YAML format, which is sensitive to spacing and indentation, specify the universe-level overrides for YB-Master and YB-TServer, as per the following example:
master: podLabels: service-type: 'database' -
Add availability zone overrides, which only apply to pods that are deployed in that specific availability zone. For example, to define overrides for the availability zone us-west-2a, you would click Add Availability Zone and use the text area to insert YAML in the following form:
us-west-2a: master: podLabels: service-type: 'database'If you specify conflicting overrides, YugabyteDB Anywhere would use the following order of precedence: universe availability zone-level overrides, universe-level overrides, provider overrides.
-
Select Force Apply if you want to override any previous overrides.
-
Click Validate & Save.
If there are any errors in your overrides definitions, a detailed error message is displayed. You can correct the errors and try to save again. To save your Kubernetes overrides regardless of any validation errors, select Force Apply.
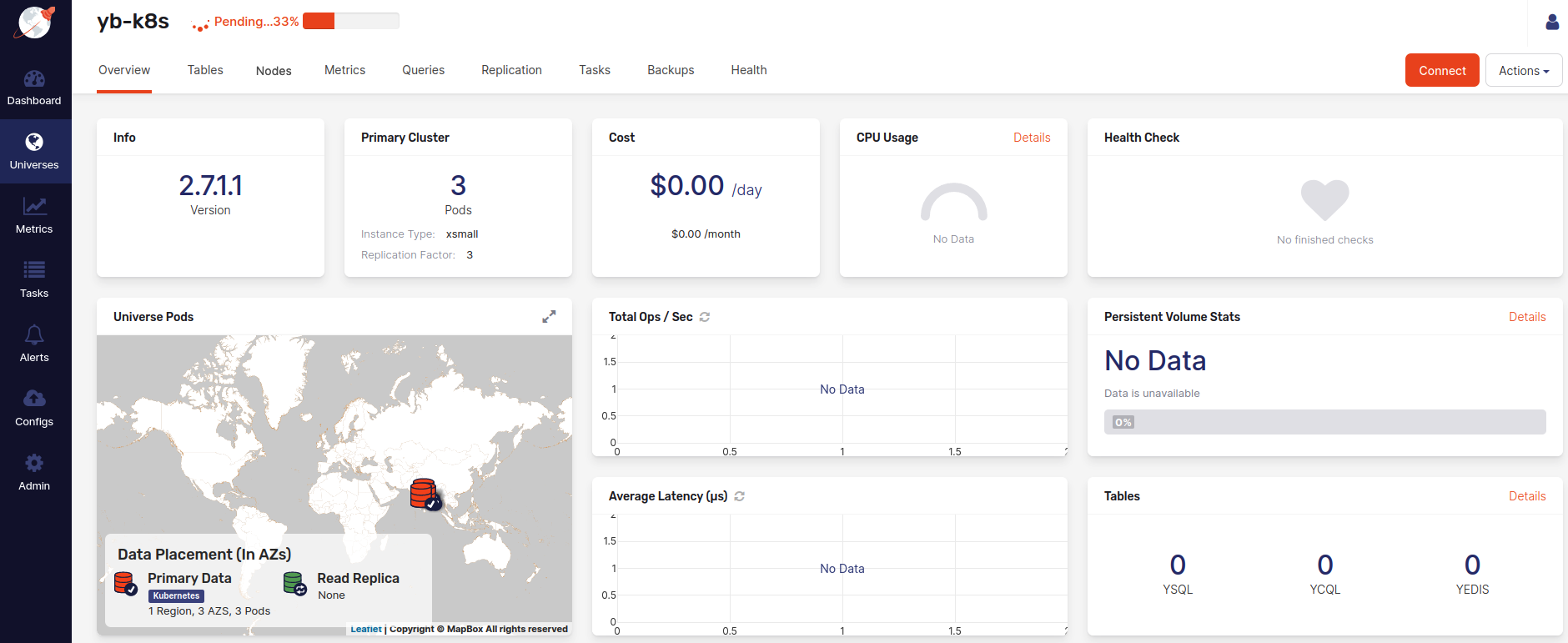
The final step is to click Create and wait for the YugabyteDB cluster to appear.
The following illustration shows the universe in its pending state:
Examine the universe and connect to nodes
The universe view consists of several tabs that provide different information about this universe.
The following illustration shows the Overview tab of a newly-created universe:
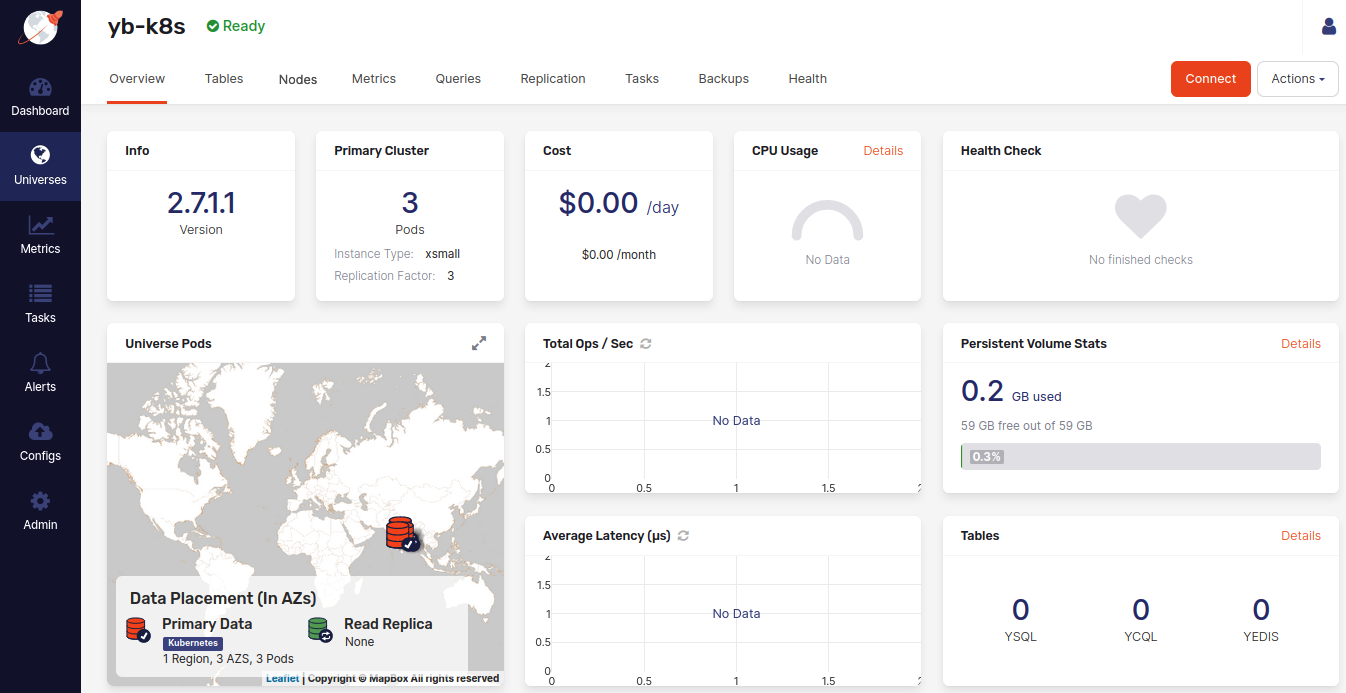
If you have defined Helm overrides for your universe, you can modify them at any time through Overview by clicking Actions > Edit Kubernetes Overrides.
The following illustration shows the Nodes tab that allows you to see a list of nodes with their addresses:
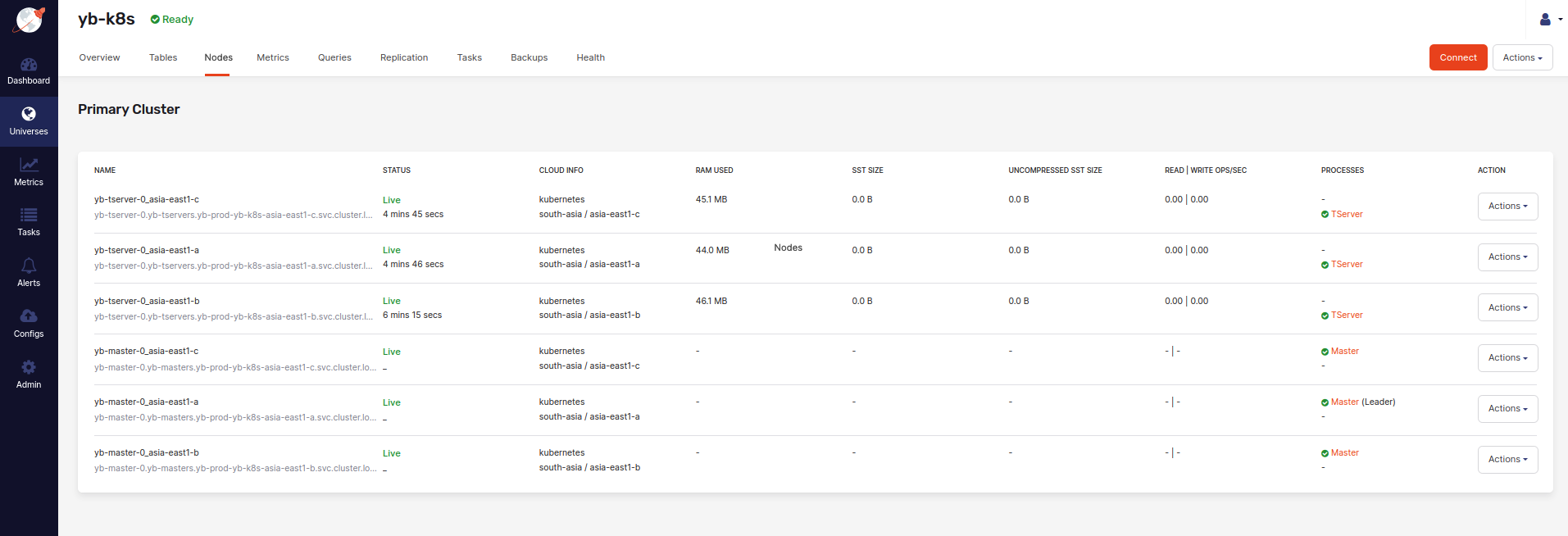
You can create a connection to a node as follows:
-
Click Connect to access the information about the universe's endpoints to which to connect.
-
On a specific node, click Actions > Connect to access the
kubectlcommands that you need to copy and use to connect to the node.
Connect to the universe
For information on how to connect to the universe from the Kubernetes cluster, as well as remotely, see Connect YugabyteDB clusters.
Create common YB-TServer service for zones
By default, each zone has its own YB-TServer service, and you can use this service to connect to the universe. Optionally, you can create an additional highly available common service across all zones as follows.
Note that this requires all the zone deployments to be in the same namespace.
-
Set the following Kubernetes overrides to add the universe-name label on the YB-TServer pods. You can do this when you create the universe or by modifying the Kubernetes overrides of an existing universe.
tserver: podLabels: universe-name: yb-k8s -
Save the following to a file named
yb-tserver-common-service.yaml. You can customize the service type, annotations, and the label selector as required.# yb-tserver-common-service.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: yb-k8s-common-tserver labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: yb-tserver # annotations: # networking.gke.io/load-balancer-type: "Internal" spec: type: ClusterIP selector: app.kubernetes.io/name: yb-tserver # This value should match with the value from step 1. universe-name: yb-k8s ports: # Modify the ports if using non-standard ports. - name: tcp-yedis-port port: 6379 - name: tcp-yql-port port: 9042 - name: tcp-ysql-port port: 5433 -
Run the following command to create the service in the universe's namespace (
yb-prod-yb-k8sin this example).$ kubectl apply -f yb-tserver-common-service.yaml -n yb-prod-yb-k8s
After the service YAML is applied, in this example you would access the universe at yb-k8s-common-tserver.yb-prod-yb-k8s.svc.cluster.local.