Scale and configure clusters
YugabyteDB Managed supports both horizontal and vertical scaling of clusters. If your workloads have increased, you can dynamically add nodes to a running cluster to improve latency, throughput, and memory. Likewise, if your cluster is over-scaled, you can reduce nodes to reduce costs.
You can scale the following cluster properties:
- Number of nodes (horizontal).
- Number of vCPUs per node (vertical).
- Disk size per node.
Cluster edit operations are performed using the Edit Infrastructure option under Regions on the cluster Settings > Infrastructure tab.
For clusters with Region, Availability Zone, or Node Level fault tolerance, the scaling operation is performed without any downtime, with a rolling restart of the underlying nodes.
The Regions section on the cluster Settings > Infrastructure tab summarizes the cluster configuration, including the number of nodes, vCPUs, memory, and disk per node, and VPC for each region.
Recommendations
- Most production applications require 4 to 8 vCPUs per node. Scale up smaller instance sizes; when the total number of vCPUs for your cluster exceeds 16, consider scaling out. For example, if you have a 3-node cluster with 2 vCPUs per node, scale up to 8 vCPUs per node before adding nodes.
- Adding or removing nodes incurs a load on the cluster. Depending on the amount of data in your database, horizontal scaling can also take time, as adding or removing nodes requires moving data between nodes. Perform scaling operations when the cluster isn't experiencing heavy traffic. Scaling during times of heavy traffic can temporarily degrade application performance and increase the length of time of the scaling operation.
- Scaling operations block other cluster operations, such as backups and maintenance. Avoid scaling operations before maintenance windows and during scheduled backups. The operation will block a backup from running.
- Before removing nodes from a cluster, make sure the reduced disk space will be sufficient for the existing and anticipated data.
Limitations
- You can horizontally scale nodes in clusters with Node Level fault tolerance in increments of 1. Nodes in clusters with Availability Zone Level fault tolerance are scaled in increments of 3 (1 per zone). Nodes in clusters with Region Level fault tolerance are scaled in increments of 1 per region.
- You can configure up to 16 vCPUs per node. To have more than 16 vCPUs per node, send your request to Yugabyte Support.
- To avoid data loss, you can only increase disk size per node; once increased, you can't reduce it.
- You can't change the fault tolerance of a cluster after it is created.
- You can't scale single node clusters (fault tolerance none), you can only increase disk size.
- You can't scale Sandbox clusters.
- If another locking cluster operation is already running, you must wait for it to finish.
- On AWS, you can't make further modifications to disk (size, IOPS) for six hours after changing either disk size or IOPS (this includes a scaling operation that increases the number of vCPUs, as this also increases disk size).
Scale and configure clusters
Single-region clusters
You can scale multi-node single-region clusters horizontally and vertically, as well as increase the disk size.
To add or remove read replicas, refer to Read replicas.
For Availability Zone Level fault tolerant clusters, you must scale nodes in increments of 3 (all zones must have the same number of nodes).
To scale a single-region cluster:
-
On the Clusters page, select your cluster.
-
Go to Settings > Infrastructure or click Actions, and choose Edit Infrastructure to display the Edit Infrastructure dialog.
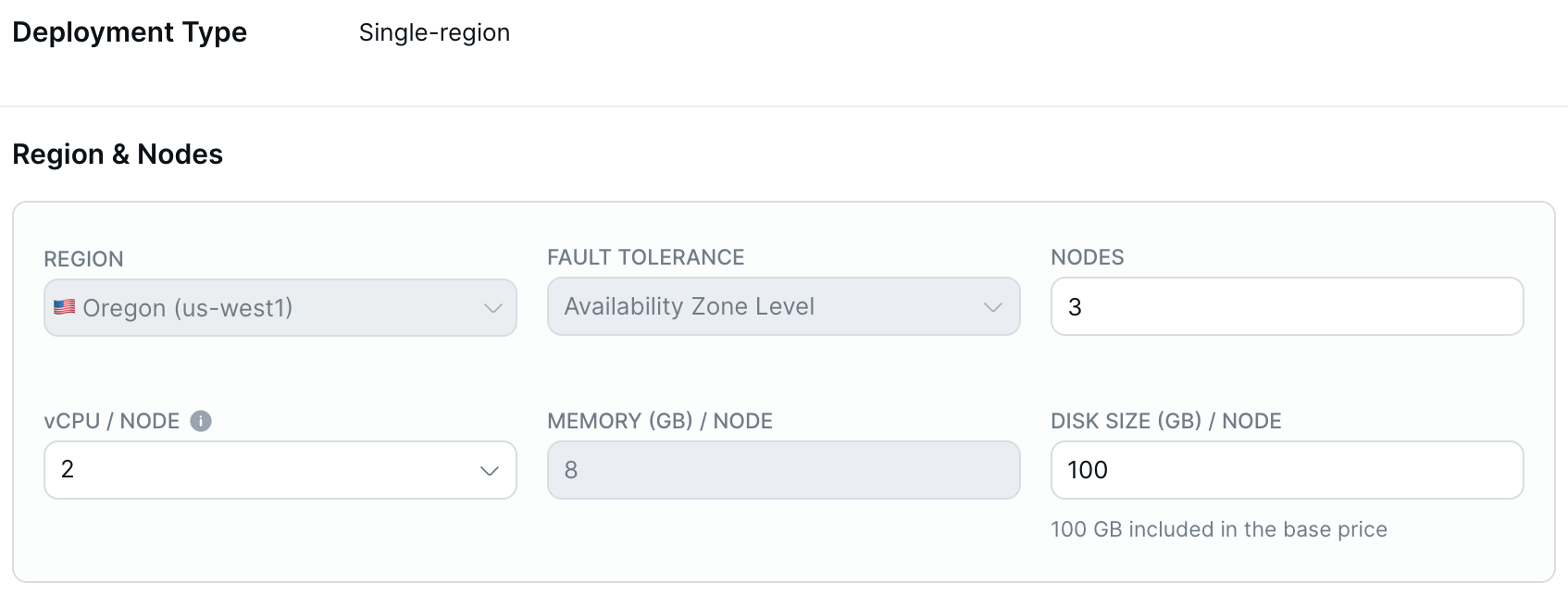
-
Enter the number of nodes, vCPUs per node, disk size in GB per node, and disk input output (I/O) operations per second (IOPS) per node (AWS only) for the cluster.
Monthly total costs for the cluster are based on the number of vCPUs and estimated automatically. + Usage refers to any potential overages from exceeding the free allowances for disk storage, backup storage, and data transfer. For information on how clusters are costed, refer to Cluster costs.
-
Click Confirm and Save Changes when you are done.
Depending on the number of nodes, whether you are adding or removing nodes, and the amount of data in your database, a horizontal scaling operation can take minutes or hours, during which time some cluster operations will not be available.
Replicate-across-regions clusters
You can scale multi-region replicated clusters horizontally and vertically, as well as increase the disk size.
To add or remove read replicas, refer to Read replicas.
To scale nodes in a replicate-across-regions cluster:
-
On the Clusters page, select your cluster.
-
Go to Settings > Infrastructure or click Actions, and choose Edit Infrastructure to display the Edit Infrastructure dialog.
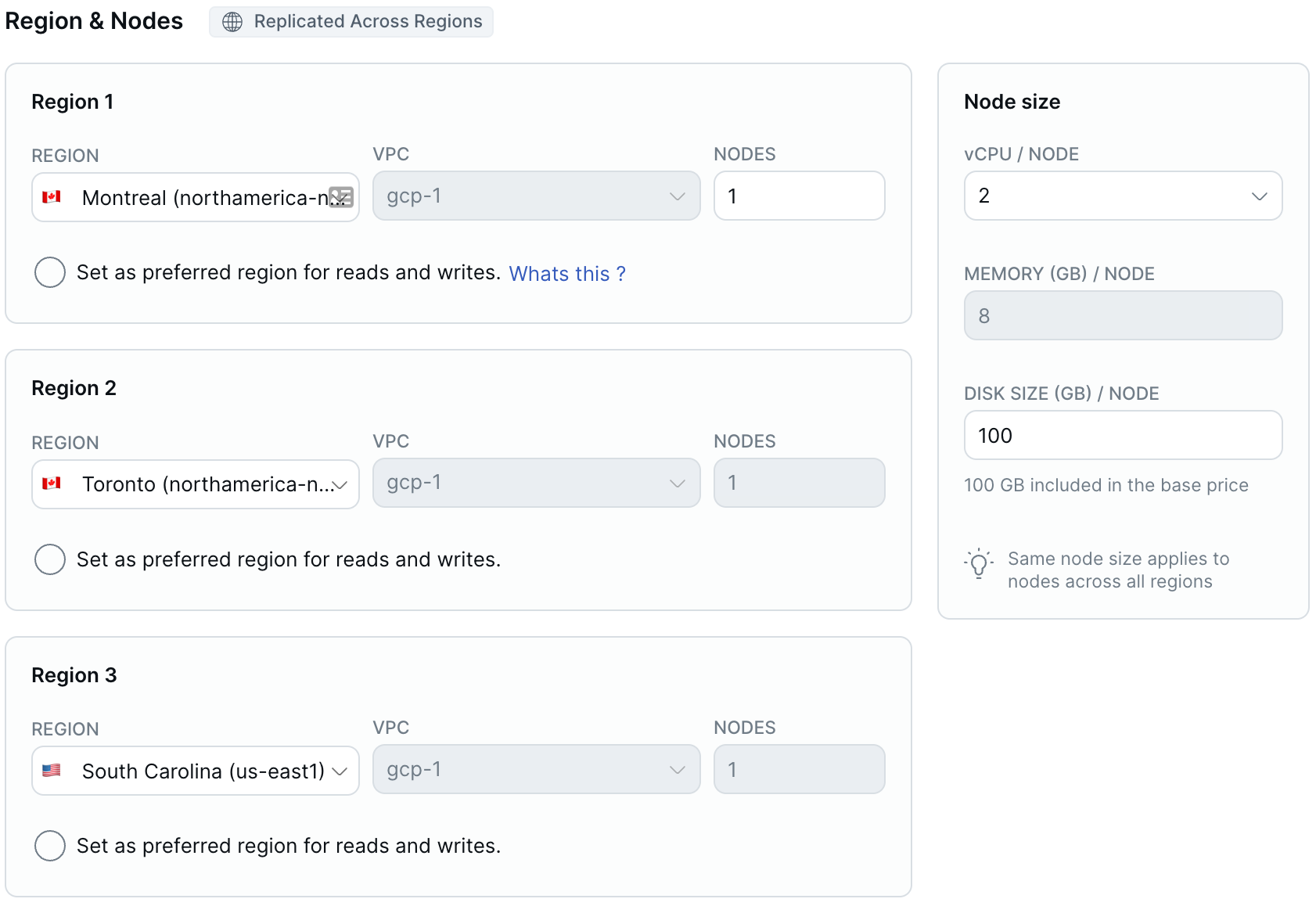
-
Enter the number of nodes, vCPUs per node, disk size in GB per node, and disk input output (I/O) operations per second (IOPS) per node (AWS only) for the cluster.
The same number of nodes and node sizes apply across all regions.
Monthly total costs for the cluster are based on the number of vCPUs and estimated automatically. + Usage refers to any potential overages from exceeding the free allowances for disk storage, backup storage, and data transfer. For information on how clusters are costed, refer to Cluster costs.
-
Optionally, set or change the Preferred region.
-
Click Confirm and Save Changes when you are done.
Depending on the number of nodes, the scaling operation can take several minutes or more, during which time some cluster operations will not be available.
Partition-by-region cluster
You can scale partition-by-region clusters horizontally and vertically.
In addition, you can add and delete regions.
New regions must be deployed in a VPC. New regions have the same fault tolerance as the primary cluster. YugabyteDB Managed automatically creates tablespaces in the new regions named region_name_ts. For example, if you add the us-central1 region, the tablespace is named us_central1_ts.
Before you can delete a region, you must drop all the tablespaces located in the region. You can't delete the primary region.
For Availability Zone Level fault tolerant clusters, you must scale nodes in each region in increments of 3.
To scale a partition-by-region cluster:
-
On the Clusters page, select your cluster.
-
Go to Settings > Infrastructure or click Actions, and choose Edit Infrastructure to display the Edit Infrastructure dialog.
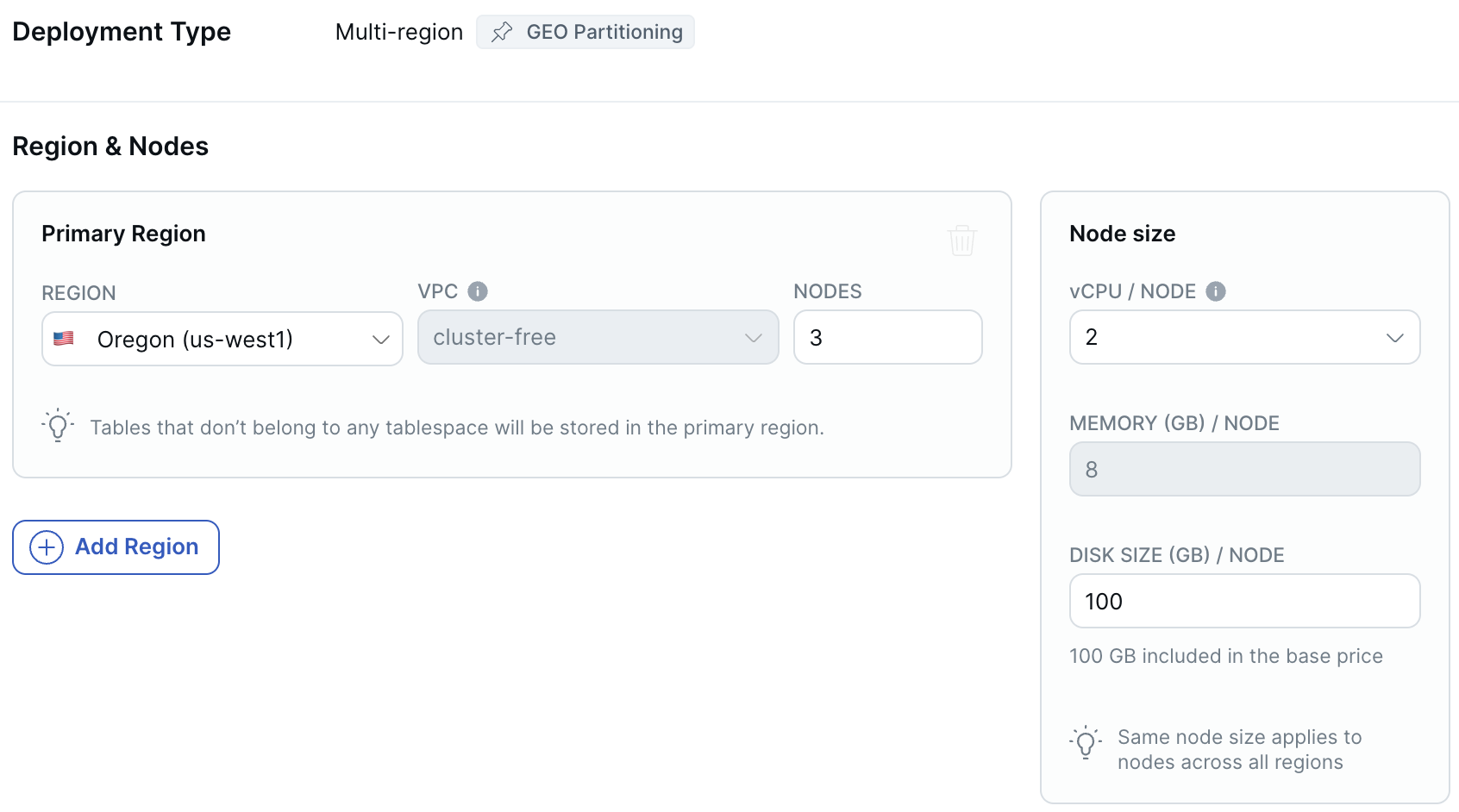
-
To add a region, click Add Region, choose the region, select the VPC where you want to deploy the cluster, and enter the number of nodes. The new region has the same fault tolerance as the primary cluster.
-
To scale the cluster horizontally, enter the number of nodes for each region.
-
To scale the cluster vertically, enter the number of vCPUs per node, disk size in GB per node, and disk input output (I/O) operations per second (IOPS) per node (AWS only).
You can scale the number of nodes in each region independently, however the same node sizes apply across all regions.
Monthly total costs for the cluster are based on the number of vCPUs and estimated automatically. + Usage refers to any potential overages from exceeding the free allowances for disk storage, backup storage, and data transfer. For information on how clusters are costed, refer to Cluster costs.
-
Click Confirm and Save Changes when you are done.
Depending on the number of nodes, the scaling operation can take several minutes or more, during which time some cluster operations will not be available.