Build scalable generative AI applications with Google Vertex AI and YugabyteDB
This tutorial outlines the steps required to build a scalable, generative AI application using Google Vertex AI and YugabyteDB.
Follow the guide to learn how to programmatically interface with the Google Vertex AI to generate text embeddings (a vectorized representation of the data) for each listing description, store embeddings in YugabyteDB, and perform a similarity search across a distributed YugabyteDB cluster using the pgvector extension.
The sample application we will use is a lodging recommendations service for travelers going to San Francisco.
Prerequisites
- A Google Cloud account with appropriate permissions
- gcloud CLI
- A YugabyteDB cluster running v2.19.2 or later
- Node.js v18 or later
- The latest version of Docker
- ysqlsh or psql
Set up the application
Download the application and provide settings specific to your deployment:
-
Clone the repository.
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabytedb-google-vertexai-lodging-service.git -
Install the application dependencies.
cd {project_directory}/backend npm install cd {project_directory}/frontend npm install -
Configure the application environment variables in
{project_directory/backend/.env}.
Set up YugabyteDB
YugabyteDB introduced support for the PostgreSQL pgvector extension in v2.19.2. This extension makes it possible to use PostgreSQL and YugabyteDB as a vectorized database.
Start a 3-node YugabyteDB cluster in Docker (or feel free to use another deployment option):
mkdir ~/yb_docker_data
docker network create custom-network
docker run -d --name yugabytedb-node1 --net custom-network \
-p 15433:15433 -p 7001:7000 -p 9001:9000 -p 5433:5433 \
-v ~/yb_docker_data/node1:/home/yugabyte/yb_data --restart unless-stopped \
yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.19.3.0-b140 \
bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/yb_data --background=false
docker run -d --name yugabytedb-node2 --net custom-network \
-p 15434:15433 -p 7002:7000 -p 9002:9000 -p 5434:5433 \
-v ~/yb_docker_data/node2:/home/yugabyte/yb_data --restart unless-stopped \
yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.19.3.0-b140 \
bin/yugabyted start --join=yugabytedb-node1 \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/yb_data --background=false
docker run -d --name yugabytedb-node3 --net custom-network \
-p 15435:15433 -p 7003:7000 -p 9003:9000 -p 5435:5433 \
-v ~/yb_docker_data/node3:/home/yugabyte/yb_data --restart unless-stopped \
yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.19.3.0-b140 \
bin/yugabyted start --join=yugabytedb-node1 \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/yb_data --background=false
The database connectivity settings are provided in the {project_dir}/backend/.env file and do not need to be changed if you started the cluster with the preceding command.
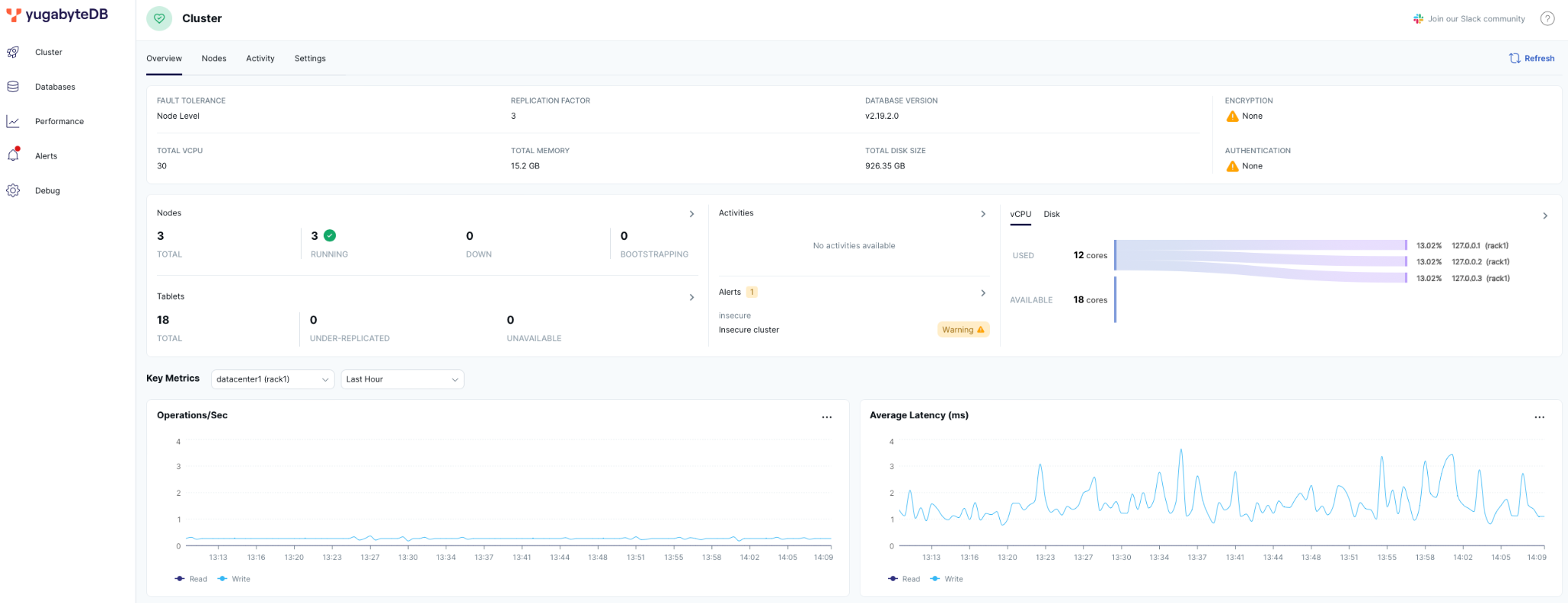
Navigate to the YugabyteDB UI to confirm that the database is up and running, at http://127.0.0.1:15433.
Load the Airbnb data set
As long as the application provides a lodging recommendation service for San Francisco, you can leverage a publicly available Airbnb data set with over 7500 relevant listings:
-
Copy the Airbnb schema and data to the first node's container:
docker cp {project_dir}/sql/0_airbnb_listings.sql yugabytedb-node1:/home docker cp {project_dir}/sql/1_airbnb_embeddings.csv yugabytedb-node1:/home -
Load the dataset to the cluster with properties in San Francisco (this can take a minute or two):
docker exec -it yugabytedb-node1 bin/ysqlsh -h yugabytedb-node1 -c '\i /home/0_airbnb_listings.sql' docker exec -it yugabytedb-node1 bin/ysqlsh -h yugabytedb-node1 \ -c "\copy airbnb_listing from /home/sf_airbnb_listings.csv with DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER" -
Add the PostgreSQL
pgvectorextension anddescription_embeddingcolumn of type vector.docker exec -it yugabytedb-node1 bin/ysqlsh -h yugabytedb-node1 -c '\i /home/1_airbnb_embeddings.sql'
Get started with Google Vertex AI
To start using Google Vertex AI in the application:
-
Create a project in Google Cloud.
-
Enable the Vertex AI API.
-
Sign in to Google Cloud via the CLI to run the application locally.
gcloud auth application-default login -
Update the Google Vertex AI environment variables in
{project_dir}/backend/.env.
Generate embeddings for Airbnb listings
Airbnb listings provide a detailed property description including number of rooms, types of amenities, a location, and other features. That information is stored in the description column and is a perfect fit for the similarity search against user prompts. However, to enable the similarity search, each description first needs to be transformed into its vectorized representation.
The application comes with the embeddings generator ({project_dir}backend/embeddings_generator.js) that creates embeddings for all Airbnb properties descriptions.
Execute the embeddingsGenerator.js script to generate embeddings in Google Vertex AI for each property, and store them in the description_embedding column in the database.
Note that it can take 10+ minutes to generate embeddings for more than 7500 Airbnb properties.
node {project_directory}/backend/vertex/embeddingsGenerator.js
....
Processing rows starting from 34746755
Processed 7551 rows
Processing rows starting from 35291912
Finished generating embeddings for 7551 rows
Start the application
With the Airbnb data with embeddings loaded in YugabyteDB, start to explore the application:
-
Start the Node.js backend.
cd {project_dir}/backend npm start -
Start the React frontend:
cd {project_dir}/frontend npm run dev
The application UI should display, and is available at the address http://localhost:3000/.
Test the application
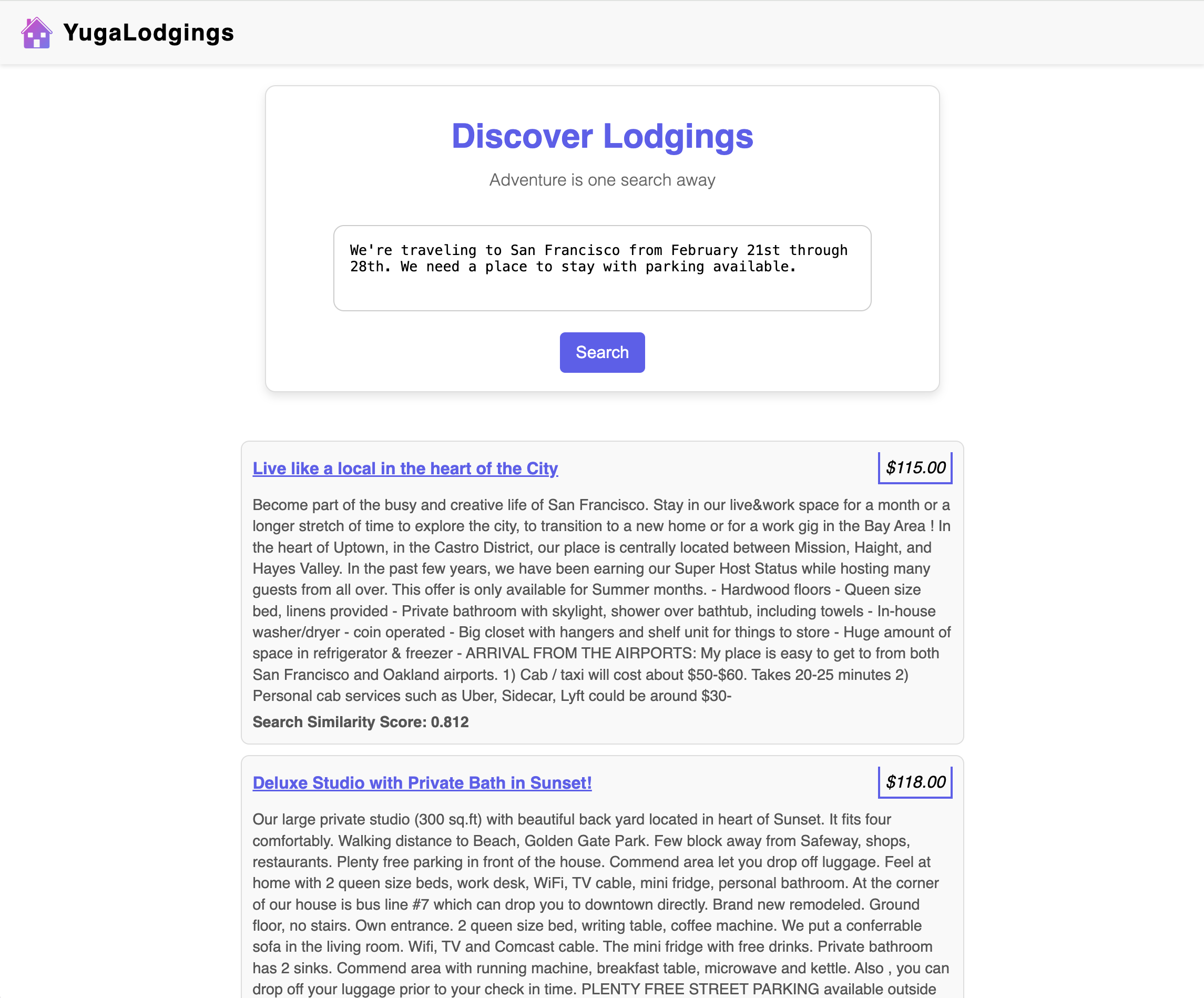
Test the application with relevant prompts. For instance:
-
We're traveling to San Francisco from February 21st through 28th. We need a place to stay with parking available.
-
I'm looking for an apartment near the Golden Gate Bridge with a nice view of the Bay.
-
Full house with ocean views for a family of 6.
-
Room for 1 in downtown SF, walking distance to Moscone Center.
These prompts are first sent to Vertex AI to be converted to embeddings. Next, the returned embeddings are used to search for similar properties, stored in YugabyteDB.
const dbRes = await pool.query(
"SELECT name, description, price, 1 - (description_embedding <=> $1) as similarity " +
"FROM airbnb_listing WHERE 1 - (description_embedding <=> $1) > 0.7 ORDER BY similarity DESC LIMIT 5",
[embeddings]
);
Wrap-up
The Google Vertex AI service simplifies the process of designing, building, and productizing generative AI applications by offering developer APIs for various major programming languages.
With the help of the PostgreSQL pgvector extension, YugabyteDB enhances the scalability of these applications by distributing data and embeddings across a cluster of nodes, facilitating similarity searches on a large scale.
To learn how to run this application using Azure, see Build scalable generative AI applications with Azure OpenAI and YugabyteDB.