Use Azure App Service with YugabyteDB
In this tutorial we'll walk you through the steps to build and deploy a scalable web application using YugabyteDB and Azure App Service.
Deploying to Azure App Service allows developers to leverage cloud infrastructure and build more scalable and available applications. Connecting these applications to YugabyteDB extends this scalability and reliability into the data layer!
In the following sections, you will:
- Examine YB Shoes, a sample eCommerce dashboard application.
- Create a web application on Azure App Service.
- Provision a database cluster on YugabyteDB Managed and seed it with data.
- Deploy YB Shoes to Azure App Service from a local repository.
Prerequisites
- A YugabyteDB Managed account. Sign up for a free trial.
- An Azure Cloud account with permission to create services.
- Azure CLI
Introducing YB Shoes
Let's start by introducing YB Shoes and its functionality. YB Shoes is an eCommerce dashboard that displays current shoe inventory and recent sales. YB Shoes is backed by a Node.js server which connects to YugabyteDB Managed. The queried inventory and sales data is displayed on a ReactJS frontend.
Visit GitHub to download the web application you will be deploying to Azure App Service.
Here's the application in action, after deploying to Azure App Service.
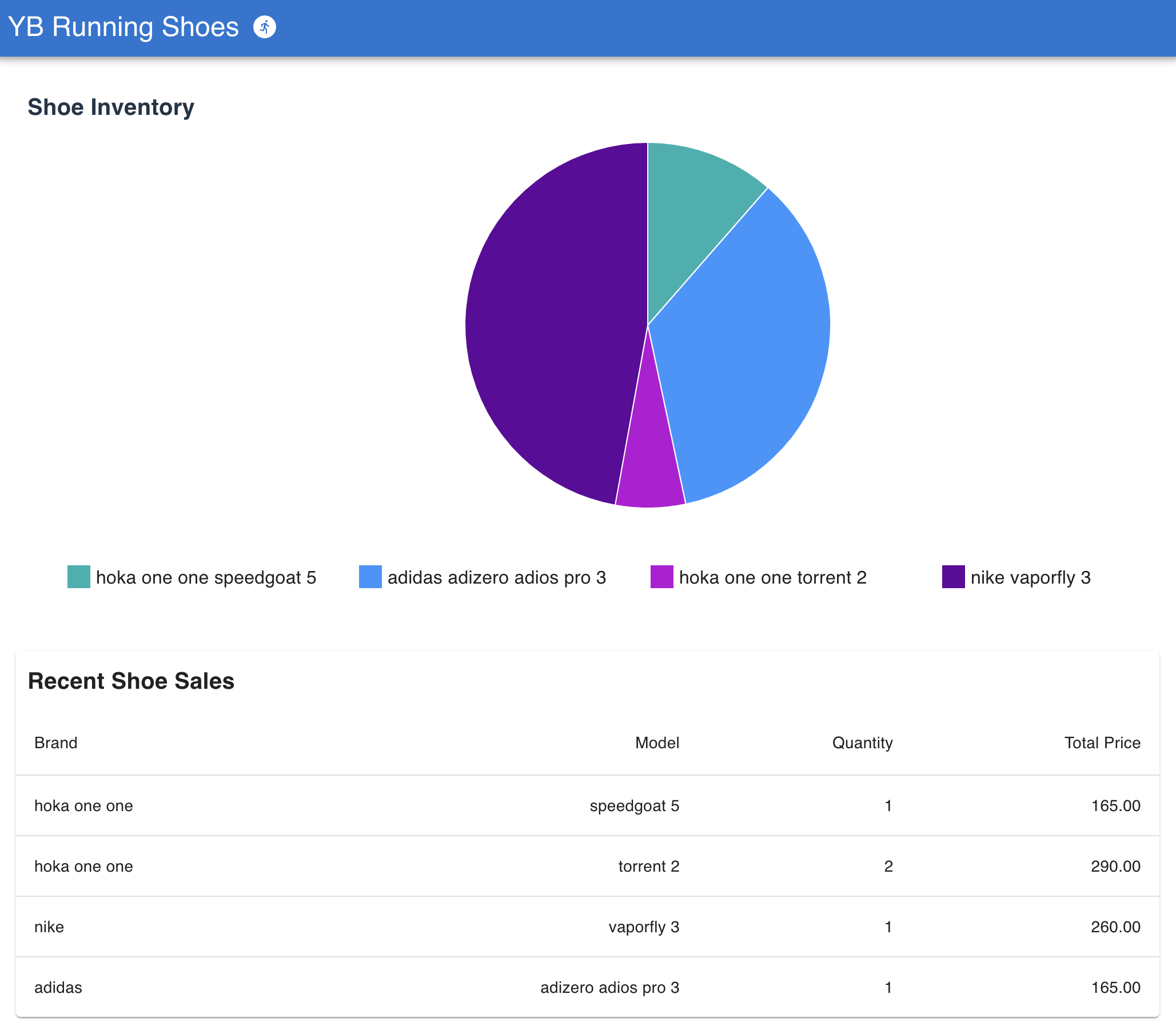
Let's cover the components required to build and deploy this application.
Create a web app on Azure App Service
With Azure App Service, developers can deploy applications in a variety of programming languages and application architectures. For YB Shoes, we will create a web app using Node.js.
From the Azure portal, under App Services, create a web app with Node.js as the runtime stack. This allows Azure to configure the runtime environment with Node.js and the dependencies required to run the application.
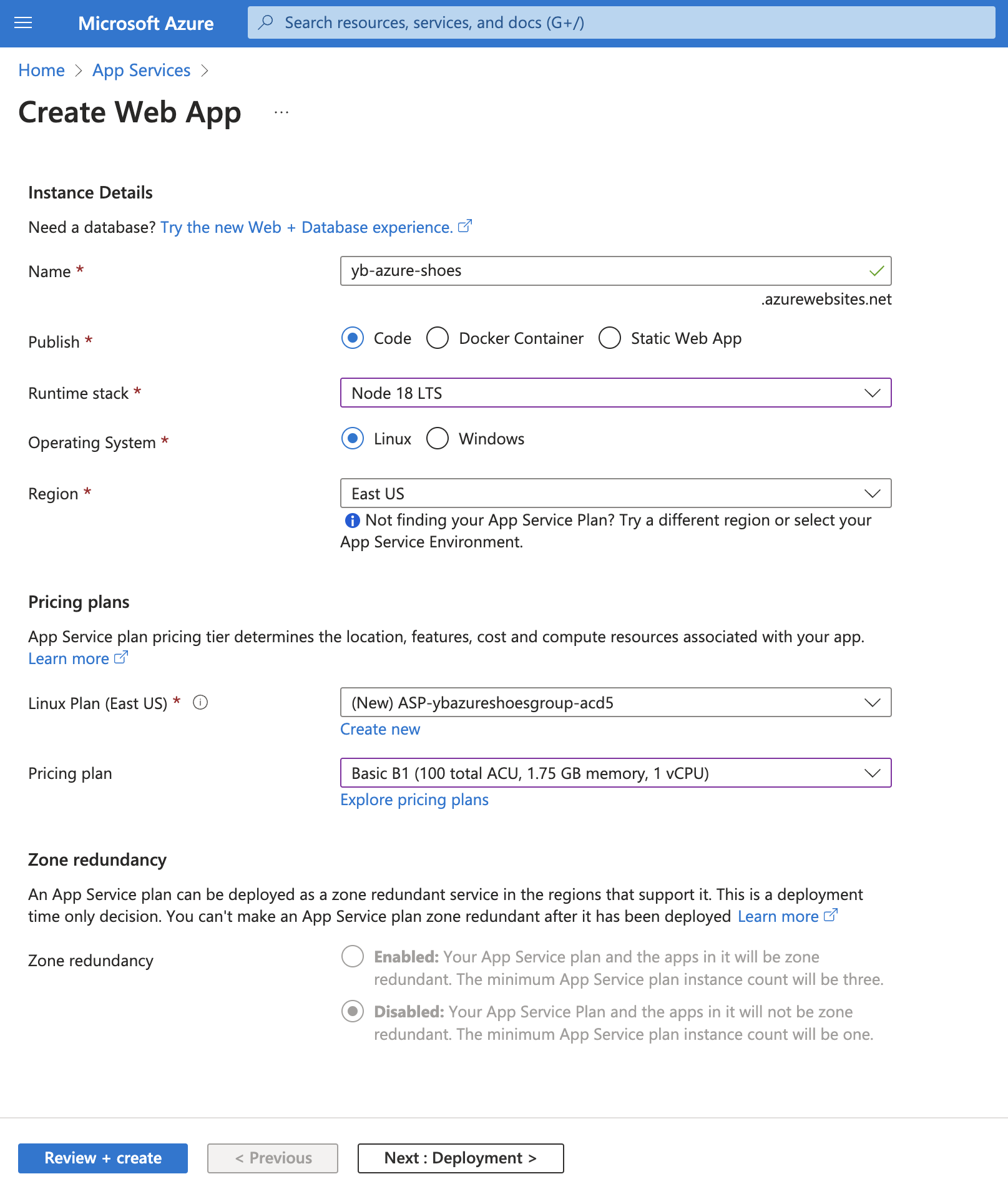
As we're deploying our application to Azure from a local repository on our machine, we can forego all settings related to continuous deployment and GitHub Actions. However, for production applications, these integrations greatly improve the development process by deploying applications to Azure automatically when the repository is updated, without the need for manual intervention.
Additionally, by selecting a free or basic tier of Azure App Service, we will deploy our application to a single zone by default. Premium pricing plans allow for multi-zone deployments for increased availability.
After creating your application, visit the associated URL to confirm it's up and running!
Now that we've set the foundation on Azure, let's deploy a database cluster for YB Shoes on YugabyteDB Managed.
Create a cluster in YugabyteDB Managed
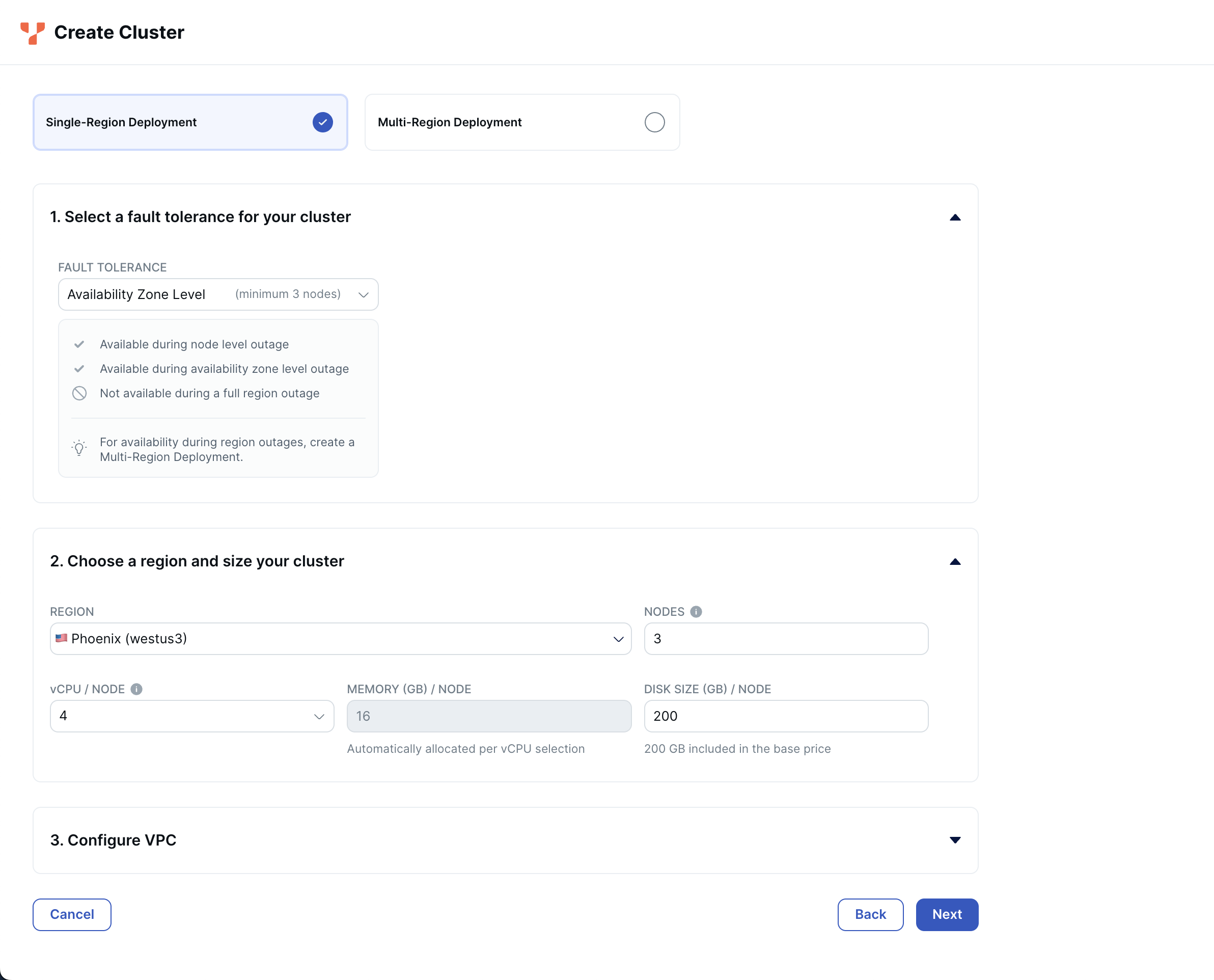
For steps on creating a cluster in YugabyteDB Managed, see the Quick start.
This example shows a three-node cluster on Azure in the westus3 region, which provides fault tolerance across availability zones, but the application also runs fine on the always-free single-node Sandbox cluster.
Add the outbound addresses for your web app to your cluster's IP allow list. Find these addresses in the Networking tab of the Azure portal. This will ensure that a connection can be made between Azure App Service and YugabyteDB.
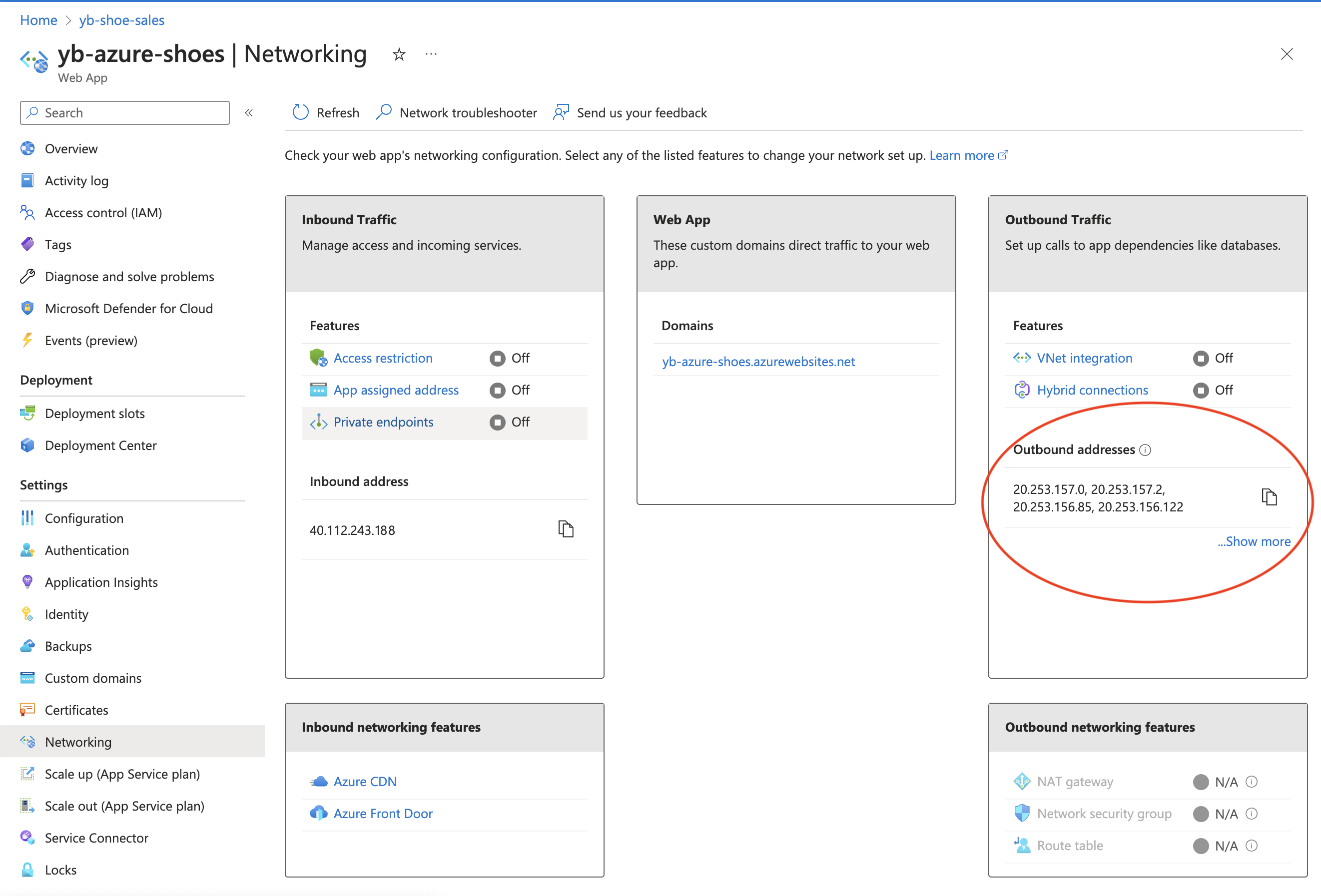
Now that we have a working cluster in YugabyteDB Managed, let's add some data.
Add data to YugabyteDB
Now that our cluster is running in the cloud, we can seed it with data using the provided schema.sql and data.sql files.
- Use the YugabyteDB Cloud Shell to connect to your cluster.
- Execute the commands in the
schema.sqlscript against your cluster. - Execute the commands in the
data.sqlscript against your cluster.
Now that your cluster is seeded with data, it's time to deploy and run the application on Azure.
Deploy YB Shoes to Azure App Service
As we're deploying the application from a local git repository, let's use the Azure CLI. It's also worth noting that Azure has a powerful extension for Visual Studio Code, which can execute the same commands.
First, you need to configure the application settings in Azure:
# Convert the downloaded CA certificate from YugabyteDB Managed to a single line string, then Base64 encode it
# Azure Configuration Settings forbid special characters, so this ensures the cert can be passed properly to our application
# Tip: Run this command to convert cert file to base64 encoded single line string:
# cat /path/to/cert/file | base64
az webapp config appsettings set -g GROUP_NAME -n APPLICATION_NAME --setting DB_HOST=[YB_DB_HOST] DB_USERNAME=admin DB_PASSWORD=[YB_DB_PASSWORD] DB_CERTIFICATE=[BASE_64_ENCODED_DB_CERTIFICATE]
After you execute this command, you can view the configuration settings in Azure portal.
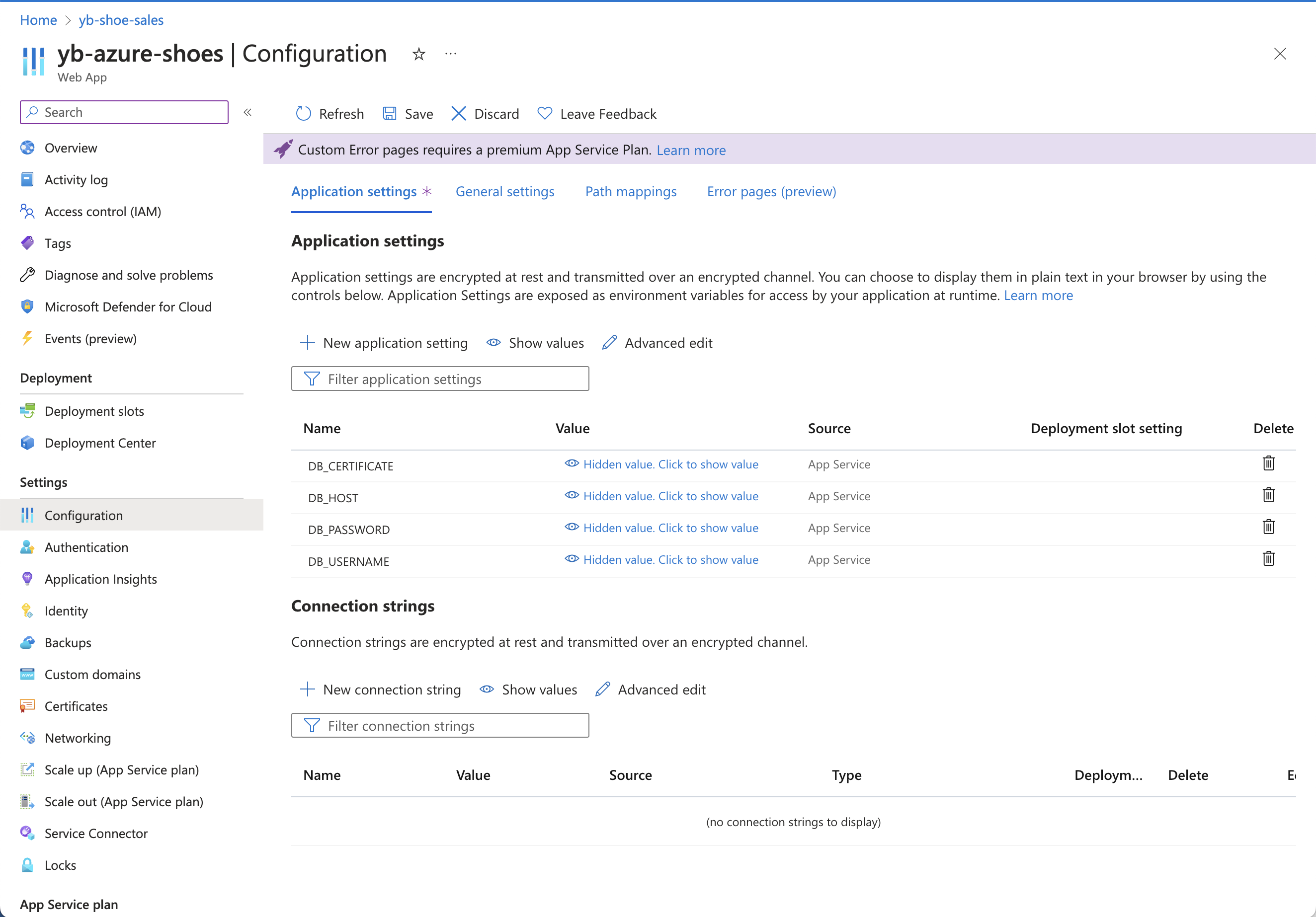
Next, use the Azure CLI to deploy your application code to the cloud, as follows:
-
In the Azure Deployment Center, configure your Local Git / FTPS Credentials under User Scope.
-
Configure the project for local git deployment as follows:
az webapp deployment source config-local-git --name APPLICATION_NAME --resource-group RESOURCE_GROUPThis outputs the git URL, similar to the following:
{ "url": "https://bhoyer@yb-shoe-sales.scm.azurewebsites.net/yb-shoe-sales.git" } -
Set git remote for Azure using the URL from previous output.
git remote add azure https://bhoyer@yb-shoe-sales.scm.azurewebsites.net/yb-shoe-sales.git -
Push to the Azure remote.
git push azure main:master
After pushing code to the remote repository, Azure automatically builds and publishes the application. Once this is complete, visit your application's default domain to view YB Shoes, running in the Azure cloud infrastructure!
Wrap-up
As you see, moving an application to the cloud with Azure App Service and YugabyteDB Managed doesn't require much additional configuration. For more insight into building Node.js applications with YugabyteDB, check out Node.js Smart Drivers for YugabyteDB: Why You Should Care.