Quick start
The local cluster setup on a single host is intended for development and learning. For production deployment, performance benchmarking, or deploying a true multi-node on multi-host setup, see Deploy YugabyteDB.
Note that the Docker option to run local clusters is recommended only for advanced Docker users. This is due to the fact that running stateful applications such as YugabyteDB in Docker is more complex and error-prone than running stateless applications.
Install YugabyteDB
Prerequisites
Before installing YugabyteDB, ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your localhost. To download and install Docker, select one of the following environments:
Install
Pull the YugabyteDB container by executing the following command:
docker pull yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.19.3.0-b140
Create a local cluster
Use the yugabyted utility to create and manage universes.
To create a 1-node cluster with a replication factor (RF) of 1, run the following command:
docker run -d --name yugabyte -p7000:7000 -p9000:9000 -p15433:15433 -p5433:5433 -p9042:9042 \
yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.19.3.0-b140 bin/yugabyted start \
--background=false
If you are running macOS Monterey, replace -p7000:7000 with -p7001:7000. This is necessary because Monterey enables AirPlay receiving by default, which listens on port 7000. This conflicts with YugabyteDB and causes yugabyted start to fail unless you forward the port as shown. Alternatively, you can disable AirPlay receiving, then start YugabyteDB normally, and then, optionally, re-enable AirPlay receiving.
Run the following command to check the container status:
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c1c98c29149b yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.19.3.0-b140 "/sbin/tini -- bin/y…" 7 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:5433->5433/tcp, 6379/tcp, 7100/tcp, 0.0.0.0:7000->7000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, 7200/tcp, 9100/tcp, 10100/tcp, 11000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9042->9042/tcp, 0.0.0.0:15433->15433/tcp, 12000/tcp yugabyte
Run the following command to check the cluster status:
docker exec -it yugabyte yugabyted status
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| yugabyted |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Status : Running. |
| Replication Factor : 1 |
| YugabyteDB UI : http://172.17.0.2:15433 |
| JDBC : jdbc:postgresql://172.17.0.2:5433/yugabyte?user=yugabyte&password=yugabyte |
| YSQL : bin/ysqlsh -h 172.17.0.2 -U yugabyte -d yugabyte |
| YCQL : bin/ycqlsh 172.17.0.2 9042 -u cassandra |
| Data Dir : /root/var/data |
| Log Dir : /root/var/logs |
| Universe UUID : f4bae205-4b4f-4dcc-9656-a04354cb9301 |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Run Docker in a persistent volume
In the preceding docker run command, the data stored in YugabyteDB does not persist across container restarts. To make YugabyteDB persist data across restarts, you can add a volume mount option to the docker run command, as follows:
-
Create a
~/yb_datadirectory by executing the following command:mkdir ~/yb_data -
Run Docker with the volume mount option by executing the following command:
docker run -d --name yugabyte \ -p7000:7000 -p9000:9000 -p15433:15433 -p5433:5433 -p9042:9042 \ -v ~/yb_data:/home/yugabyte/yb_data \ yugabytedb/yugabyte:latest bin/yugabyted start \ --base_dir=/home/yugabyte/yb_data \ --background=falseIf running macOS Monterey, replace
-p7000:7000with-p7001:7000.
Connect to the database
The cluster you have created consists of two processes:
- YB-Master keeps track of various metadata (list of tables, users, roles, permissions, and so on).
- YB-TServer is responsible for the actual end user requests for data updates and queries.
Using the YugabyteDB SQL shell, ysqlsh, you can connect to your cluster and interact with it using distributed SQL. ysqlsh is installed with YugabyteDB and is located in the bin directory of the YugabyteDB home directory.
To open the YSQL shell, run ysqlsh.
docker exec -it yugabyte bash -c '/home/yugabyte/bin/ysqlsh --echo-queries --host $(hostname)'
ysqlsh (11.2-YB-2.19.3.0-b0)
Type "help" for help.
yugabyte=#
To load sample data and explore an example using ysqlsh, refer to Retail Analytics.
Monitor your cluster
When you start a cluster using yugabyted, you can monitor the cluster using the YugabyteDB UI, available at localhost:15433.
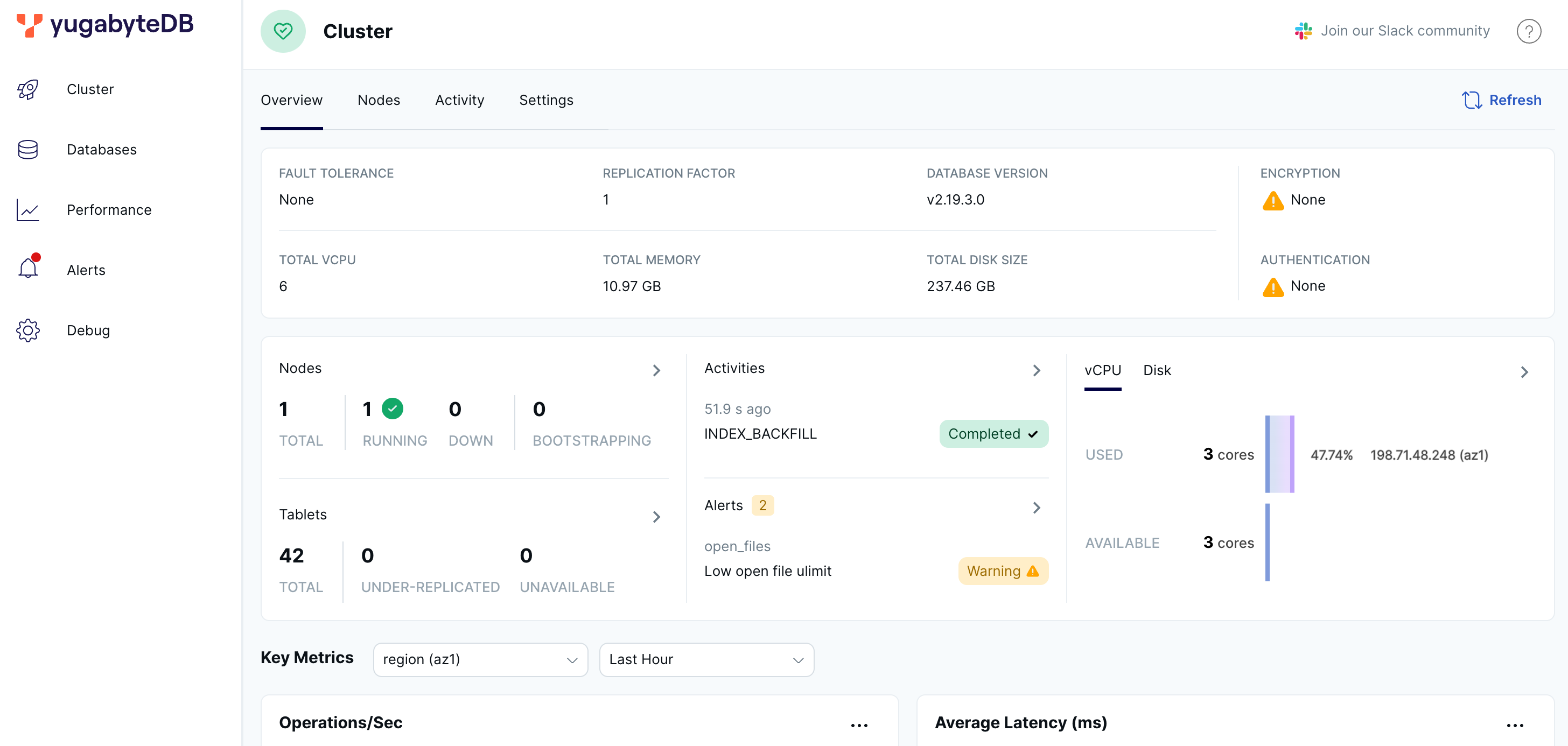
The YugabyteDB UI provides cluster status, node information, performance metrics, and more.