Continuous availability
YugabyteDB can continuously serve requests in the event of planned or unplanned outages, such as system upgrades and outages related to a node, availability zone, or region. YugabyteDB's High availability is achieved through a combination of distributed architecture, data replication, consensus algorithms, automatic rebalancing, and failure detection mechanisms, ensuring that the database remains available, consistent, and resilient to failures of fault domains.
Fault domains
A fault domain is a potential point of failure. Examples of fault domains would be nodes, racks, zones, or entire regions. YugabyteDB's RAFT-based replication and automatic rebalancing ensure that even if a domain fails, the database can continue to serve reads and writes without interruption. The fault tolerance of a YugabyteDB universe determines how resilient the universe is to domain outages. Fault tolerance is achieved by adding redundancy in the form of additional nodes across the fault domain.
Node failure
In a universe with a replication factor (RF) of 3, the fault tolerance is equal to 1 node. That is, a minimum of 3 nodes is required to tolerate 1 node outage; an RF 5 universe needs a minimum of 5 nodes to tolerate 2 node outages. Each additional node increases the resilience to node failures.
Zone failure
An RF 3 universe can survive 1 zone outage when spread across 3 zones. This setup ensures that even if an entire zone goes down, the database can continue operating.
Region failure
This is similar to zone-level fault tolerance, but on a larger scale, where nodes are spread across multiple regions. This provides the highest level of protection, providing fault tolerance against region-wide outages.
Rack failure
In the case of on-premises deployments, you can consider racks as zones to make your universe rack-aware and ensure that a universe spread across racks can survive rack-level failures.
Rack awareness
To use racks as fault domains, map them to zones using the --cloud-location flag with yugabyted, or directly using the YB-TServer --placement-zone flag.Recovery time
If a fault domain experiences a failure, an active replica is ready to take over as a new leader in a matter of seconds after the failure of the current leader and serve requests.
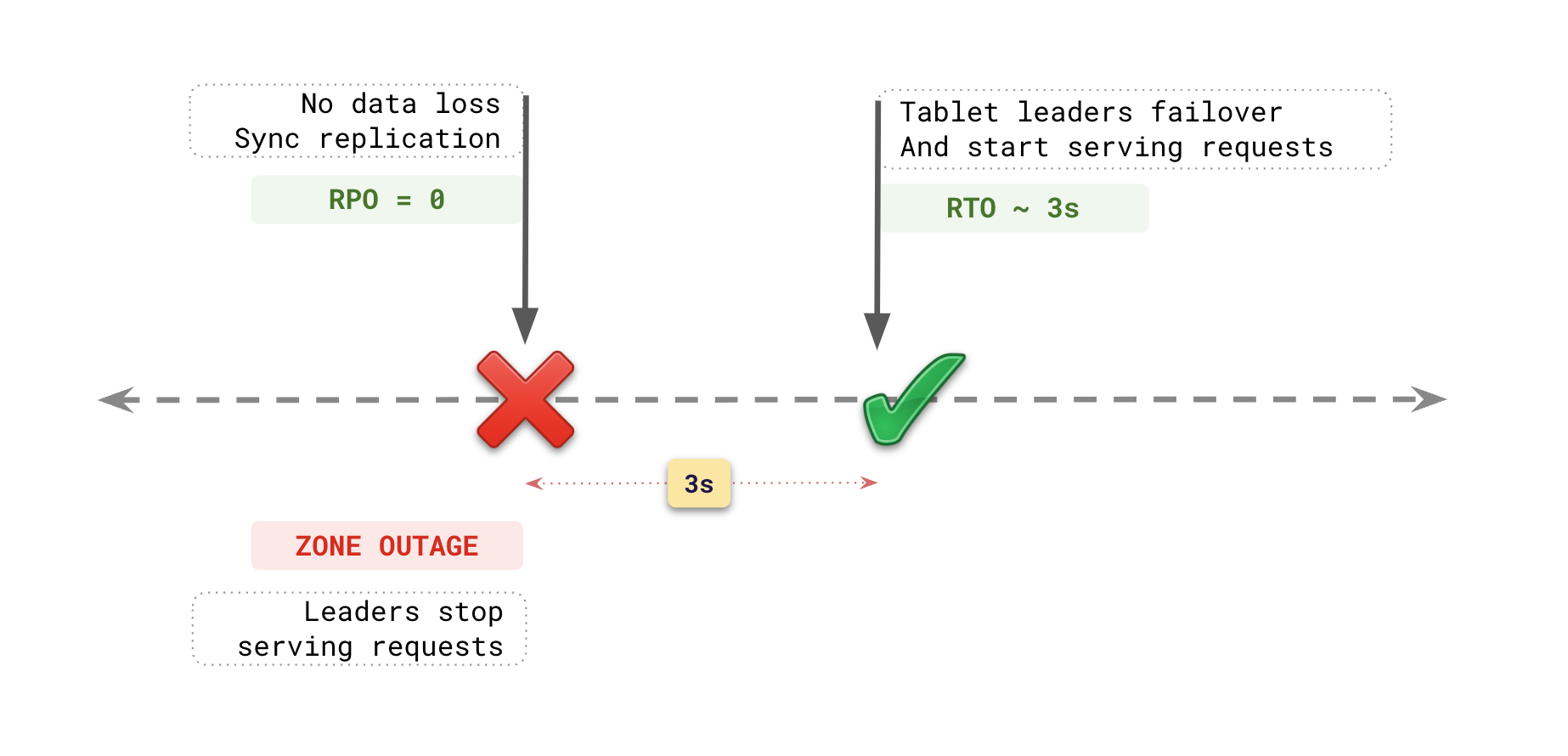
This is reflected in both the recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) for YugabyteDB universes:
- The RPO for the tablets in a YugabyteDB universe is 0, meaning no data is lost in the failover to another fault domain.
- The RTO for a zone outage is approximately 3 seconds, which is the time window for completing the failover and becoming operational out of the remaining fault domains.
YugabyteDB also provides HA of transactions by replicating the uncommitted values, also known as provisional records, across the fault domains.
The benefits of continuous availability extend to performing maintenance and database upgrades. You can maintain and upgrade your universe to a newer version of YugabyteDB by performing a rolling upgrade; that is, stopping each node, upgrading the software, and restarting the node, with zero downtime for the universe as a whole.
For more information, see the following: